A student from the social work courses – Tenzin Chorran from Post Graduate Program in Development Management at ISDM’s. During the rural immersion part of the program called ‘Realising India’, she visited a village in Sehore, Madhya Pradesh, where she was appalled by the situation of women in rural hinterlands.
Rural Immersion is a critical component of ISDM’s PGP DM program. Our batch was divided into groups and sent to different districts to understand the ground realities of societies and institutions. Along with my group, I went to Sehore for two weeks. The field visits in the rural areas helped me understand the human-nature interactions where most rural communities are still dependent on their immediate natural resource environment, such as forests, for daily livelihood needs essential for survival. The close interaction with the community using Participatory Rural Appraisal (PRA) tools helped me identify the daily struggles of marginalised communities, especially rural women, and analyse their knowledge of livelihood conditions.
During one such visit, I met *Savita, a 25-year-old woman from Bhilai Khari, a tribal village in Nasrullaganj block of Sehore district in Madhya Pradesh. She wakes up at 5 am every morning, walks a few kilometres to gather some fuelwood, fetches water on the way back from the hand pump and starts cooking meals for her family on a chulha. She represents most women in her village who do this daily because half of their households do not have an LPG gas connection.
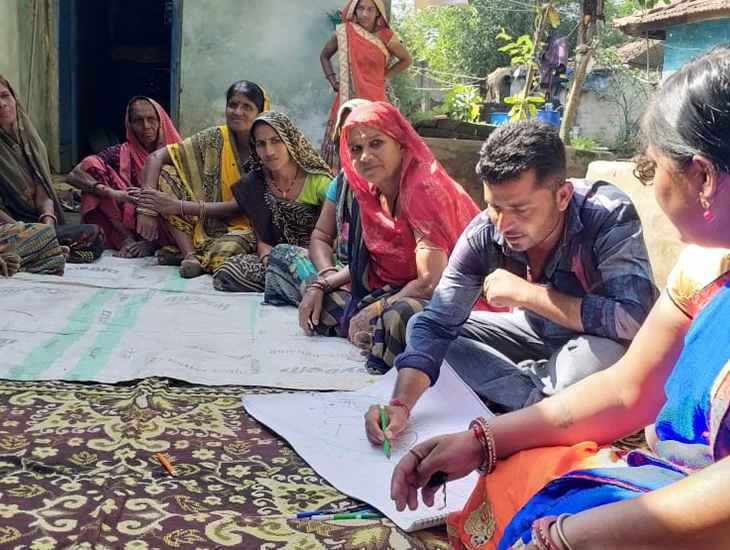

Based on conversations with other women from the community, I realised that the struggle of fetching fuelwood and water for domestic consumption is an everyday task, requiring vast amounts of physical labour. The bundle of fuelwood that these women carry ranges from 5-10 kilograms, and they usually make multiple trips to collect water from the hand pump. The summer months are typically parched, and the water in the handpump dries up, which means that these women have to travel at least three kilometres to a nearby pond to extract water.
All the households in this village have the traditional chulha, and out of 40 homes, 20 of them got the LPG connection three years ago. We gathered that this was through the government’s introduction, Ujjwala Yojana. The remaining households had their connections either wrongly delivered to other people even though they had filled the forms or refused to shift to the usage of LPG in their homes.
The Ujjwala Yojana aims to empower women and decrease drudgery by shifting to clean methods of cooking which can save time and energy and avoid health-related issues among women in rural India. Unfortunately, the scheme has been made redundant due to a lack of affordability and availability of services. The local rural communities cannot afford the refilling of the LPG cylinders due to financial restrictions, which is Rs 700/- for every refill. Almost twenty households with LPG connections have not been able to refill their cylinders due to a money crunch and rely on the chulha again. Apart from behavioural biases for the chulha preference, another reason is the inability to carry cylinders to their houses due to limited doorstep availability of services.
It is perhaps important to note a wide gap between the implementation of government schemes and the primary stakeholders’ requirements of that particular scheme. For instance, in the case of this small village in Nasrullaganj, many women like Savita might not be able to benefit from the Ujjwala Yojana, considering innumerable gaps which presently exist. Addressing these gaps, and effective community participation should encourage the bottom-up decision-making processes. Policymakers partnering with the government need to stress the importance of evidence-based decision making. The focus here should be evidence collection through the participatory method, constantly rechecking and evaluating the reach of social security schemes to ensure their success
If you are considering a career in Social Sector, it might be worth your while to look into PGP -DM program offered by ISDM. You can find more information about the program here:
Tenzin Chorran
*All names have been changed to protect identities